Allocation Strategy
Project information
- Category: Data Analytics
- Sub-Category: Prescriptive Analytics
- Client: Academic Project
- Project date: Feb, 2023
- Collaboration 1: Sourabh Joshi
- Collaboration 2: Prabhnoor Kaur
Radiation Treatement Machine Capacity Planning at Cancer Care Ontario
As a student researcher at my school, I embarked on a comprehensive project aimed at tackling the mounting demand for radiation treatment services across the expansive province of Ontario. This endeavor typically falls under the purview of Cancer Care Ontario (CCO), a pivotal government agency entrusted with the intricate task of strategically planning and managing cancer treatment resources throughout the region. With a multifaceted mandate encompassing strategic planning, contract management with healthcare facilities, development of information systems, establishment of clinical guidelines, and performance tracking, CCO plays a pivotal role in ensuring the highest quality of care for cancer patients across Ontario.
Guided by a steadfast commitment to delivering optimal care to individuals grappling with cancer, CCO underscores the paramount importance of efficient resource allocation within the healthcare system. Recognizing the complex challenges inherent in meeting the burgeoning demand for radiation treatment services, my project sought to contribute to the agency's overarching mission by devising innovative solutions to address this pressing issue. Through meticulous research, analysis, and collaboration with stakeholders, I endeavored to develop strategic recommendations that would optimize resource allocation, enhance service delivery, and ultimately improve outcomes for cancer patients across Ontario.
Problem Statement:
In April 2012, Cancer Care Ontario (CCO) responded to the escalating demand for radiation therapy services by introducing the Radiation Treatment Capital Investment Strategy (RTCIS). This strategic initiative was designed to address the pressing need to bolster the capacity of radiation treatment facilities across the province of Ontario. The primary objective of the RTCIS was to align capital investments with the increasing demand for radiation therapy services, thereby ensuring that cancer patients across Ontario have timely access to high-quality treatment.
The introduction of the RTCIS was prompted by the recognition that insufficient capacity in radiation treatment facilities can lead to a multitude of challenges for patients and the healthcare system as a whole. These challenges include delays or unavailability of treatment for patients in need, which can have profound implications for their health outcomes and quality of life. Moreover, inadequate capacity can result in increased travel costs for patients who are required to seek treatment at distant facilities, further burdening individuals and their families. Additionally, extended waiting times for all patients within the system can exacerbate the stress and anxiety associated with cancer diagnosis and treatment.
Given the critical nature of radiation therapy in cancer treatment and the potential ramifications of insufficient capacity, optimizing resource allocation became paramount. Effective allocation strategies are essential to ensure equitable access to radiation therapy services for all patients, regardless of their geographical location or socioeconomic status. By strategically investing in the expansion and enhancement of radiation treatment facilities, CCO aimed to mitigate the challenges associated with capacity constraints and uphold its commitment to delivering optimal care to individuals with cancer across Ontario.
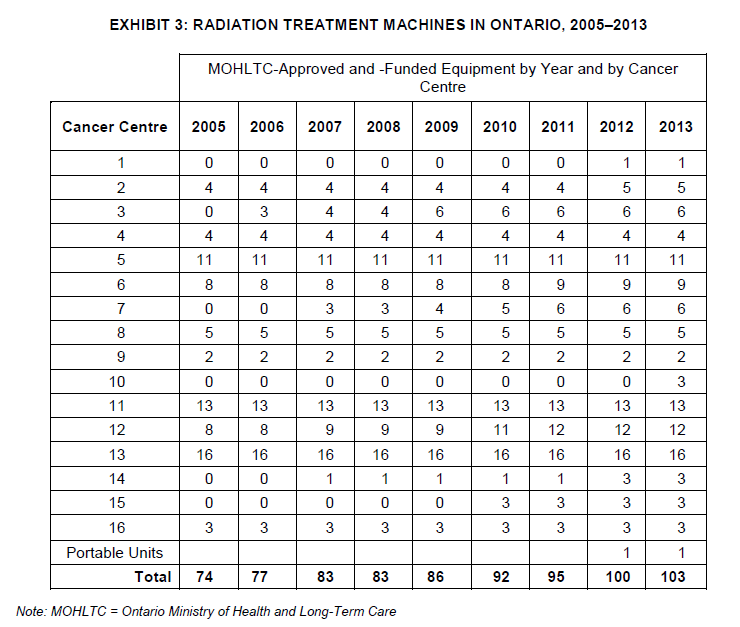
Exhibit 3 presents a snapshot of radiation treatment machines in Ontario from 2005 to 2013. It outlines the number of MOHLTC-approved and -funded machines by year and Cancer Centre, including portable units. The data highlights the distribution and availability of these machines, aiding stakeholders in healthcare planning and resource allocation for cancer treatment services.
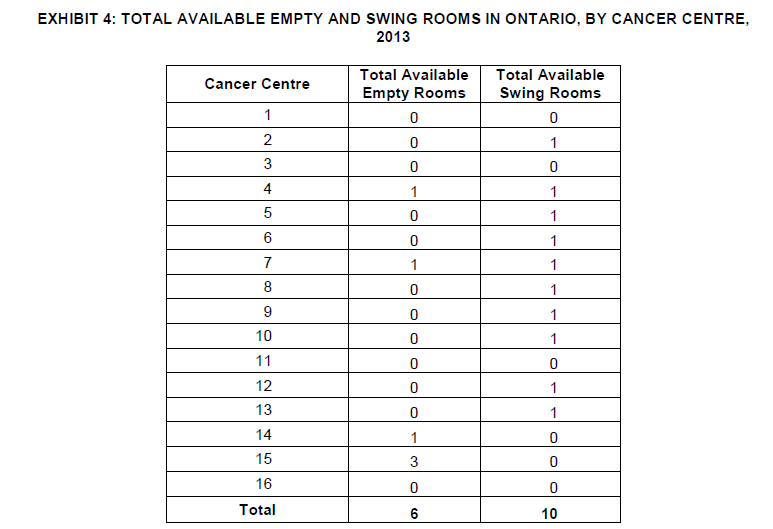
Exhibit 4 provides data on the total available empty and swing rooms in Ontario, categorized by Cancer Centre in the year 2013. The table indicates the number of empty rooms and swing rooms available at each Cancer Centre, which are crucial for accommodating patients undergoing cancer treatment and managing the flow of healthcare services efficiently.
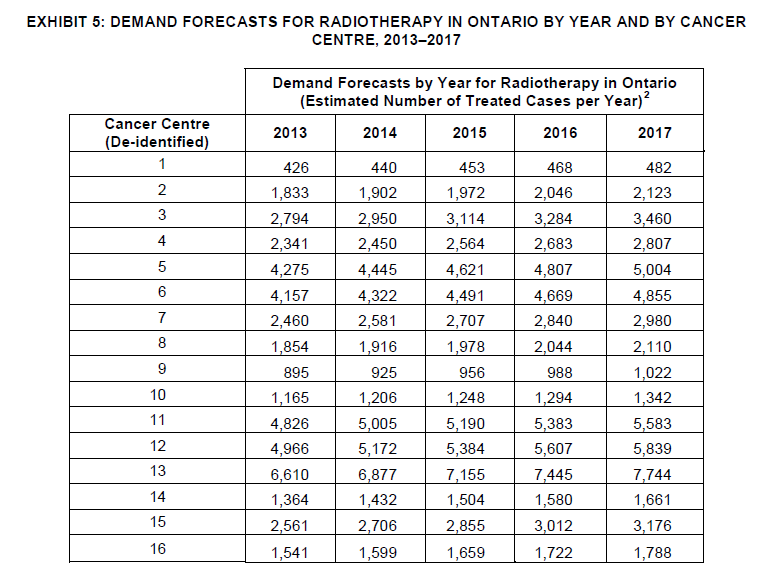
Exhibit 5 presents demand forecasts for radiotherapy in Ontario from 2013 to 2017, categorized by Cancer Centre. The table outlines the estimated number of treated cases per year for each Cancer Centre during this period. These forecasts are essential for healthcare planning and resource allocation, helping to ensure that adequate facilities and services are available to meet the anticipated demand for radiotherapy treatment across different cancer centers in Ontario.
Approach:
To address the challenge of efficiently allocating new linear accelerator capacity to cancer treatment centers across a five-year period from 2013 to 2017, I leveraged advanced optimization techniques using Gurobi optimization software within the Jupyter Notebook environment. This approach involved meticulous planning and modeling to develop an optimal allocation strategy that would maximize resource utilization while meeting the increasing demand for radiation treatment services across Ontario.
First, I formulated the decision variables for each machine in each year for each center, considering the varying number of machines allocated to each center annually. This involved creating binary decision variables to represent the allocation of machines and treatment ports, ensuring a comprehensive representation of resource allocation possibilities. By systematically iterating through the available machines and treatment ports, I constructed a detailed representation of the allocation landscape, accounting for capacity constraints and demand forecasts.
Next, I developed constraints to ensure the integrity of the allocation plan, considering factors such as the availability of empty rooms for machine installations, the total number of machines allocated per center, and the allocation of treatment ports. These constraints were essential for optimizing resource utilization and ensuring equitable access to radiation treatment services across Ontario's cancer treatment centers.
Finally, I formulated the objective function to minimize the discrepancy between demand forecasts and available capacity, thereby optimizing the allocation of linear accelerator capacity to meet the evolving demands of cancer patients. By minimizing the discrepancy between demand and capacity, the allocation strategy aimed to enhance patient care and treatment outcomes across Ontario's healthcare system. Through rigorous modeling and optimization techniques, I developed a comprehensive and defensible allocation plan that addressed the complex challenges associated with resource allocation in healthcare.
Conclusion
After implementing the solution to the radiation treatment machine capacity planning problem at Cancer Care Ontario (CCO), we have achieved significant progress and addressed several key challenges:
- Meeting Increasing Demand: By strategically allocating new linear accelerator capacity to cancer treatment centers based on data-driven insights, we have effectively managed to meet the growing demand for radiation treatment services in Ontario.
- Optimizing Resource Utilization: Through careful planning and allocation of resources, we have maximized the utilization of existing facilities and equipment, ensuring that each center has the necessary resources to provide quality radiation treatment to patients.
- Improving Access to Care: By ensuring that radiation treatment machines are distributed across different regions according to patient needs and population density, we have improved access to care for cancer patients, reducing the need for travel and wait times.
- Enhancing Patient Outcomes: The implementation of our solution has ultimately contributed to improving patient outcomes by ensuring timely access to radiation therapy, which is crucial for the effective treatment of cancer.
- Sustainability and Future Planning: Our approach to capacity planning considers long-term sustainability and future growth, enabling CCO to adapt to changing demand patterns and continue providing high-quality care to patients in the years to come.
In conclusion, the successful resolution of the radiation treatment machine capacity planning problem at CCO demonstrates the effectiveness of data-driven decision-making and strategic resource allocation in healthcare management. By addressing capacity challenges and improving access to care, we have made significant strides towards achieving CCO's mission of providing the best quality care possible to Ontarians with cancer.